
News
Study on the effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on burn wound treatment
09 Jan,2025

Autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a plasma rich in high concentrations of platelets and leukocytes extracted from autologous anticoagulated blood by centrifugation. Platelets in PRP release various growth factors and other substances after activation, which play an important role in the wound repair process by promoting cell chemotaxis, cell adhesion, cell division and proliferation, and angiogenesis. In addition, platelets themselves can secrete bactericidal proteins and also have antibacterial and pain-reducing properties.
Autologous PRP is a concentration of autologous plasma, which avoids the risk of immune rejection, disease transmission, and the impact of xenogeneic recombinant gene products on the human genetic structure. The ratio of growth factors and proteases is close to physiological ratios, which is conducive to maintaining local homeostasis. The state and various factors cooperate with each other to promote their physiological effects. The level of growth factors contained in PRP is not uniform, and its content is related to the following factors:
(1) The concentration of growth factors in platelet granules varies, and there are individual differences between different patients.
(2) Differences in technical methods for preparing PRP.
(3) The concentration of white blood cells contained in PRP is different, because white blood cells can also secrete growth factors.
(4) Differences in platelet activation.
However, there was no significant correlation between the growth factor content in whole blood or PRP and platelet count, donor age and gender. Therefore, quantitative detection of growth factors in PRP is the best quality control method for preparing PRP. In addition, PRP also contains a large number of white blood cells, which can increase local anti-infection ability.
Usually, the concentration of platelets in PRP is 2.0 to 8.5 times higher than that in ordinary plasma. However, the more platelets in PRP, the better, because some scholars have shown that high concentrations of PRP can inhibit wound repair. PRP can be used directly externally, or added to transplant materials (such as bone marrow), or directly injected into the lesion as a matrix for wound repair. PRP can exert an immediate effect, quickly stop bleeding, and promote cell adhesion by forming fibrin clots. Applying PRP to the injured area can imitate and surpass the body's physiological response to trauma, releasing high concentrations of growth factors in the injured area, which can promote tissue repair, reduce pain, reduce blood loss, etc.
Tissue repair and regeneration after burns are closely related to burn depth and early wound treatment. Deep burn wound healing can benefit from wound base neovascularization and dermal regeneration. However, for shallower burn wounds, rapid re-epithelialization is more important for this type of wound healing. PRP helps form a vascularized matrix, which can promote the survival of skin grafts in deep second and third-degree burn wounds, and PRP can provide better growth conditions for dermal substitutes. Therefore, PRP may play a positive role in the healing of deep second and third-degree burn wounds. Autologous PRP is derived from one's own body and is a relatively safe product. There are currently no reports of adverse reactions and toxic effects caused by PRP. Therefore, PRP has good application prospects in the field of burn wound repair.
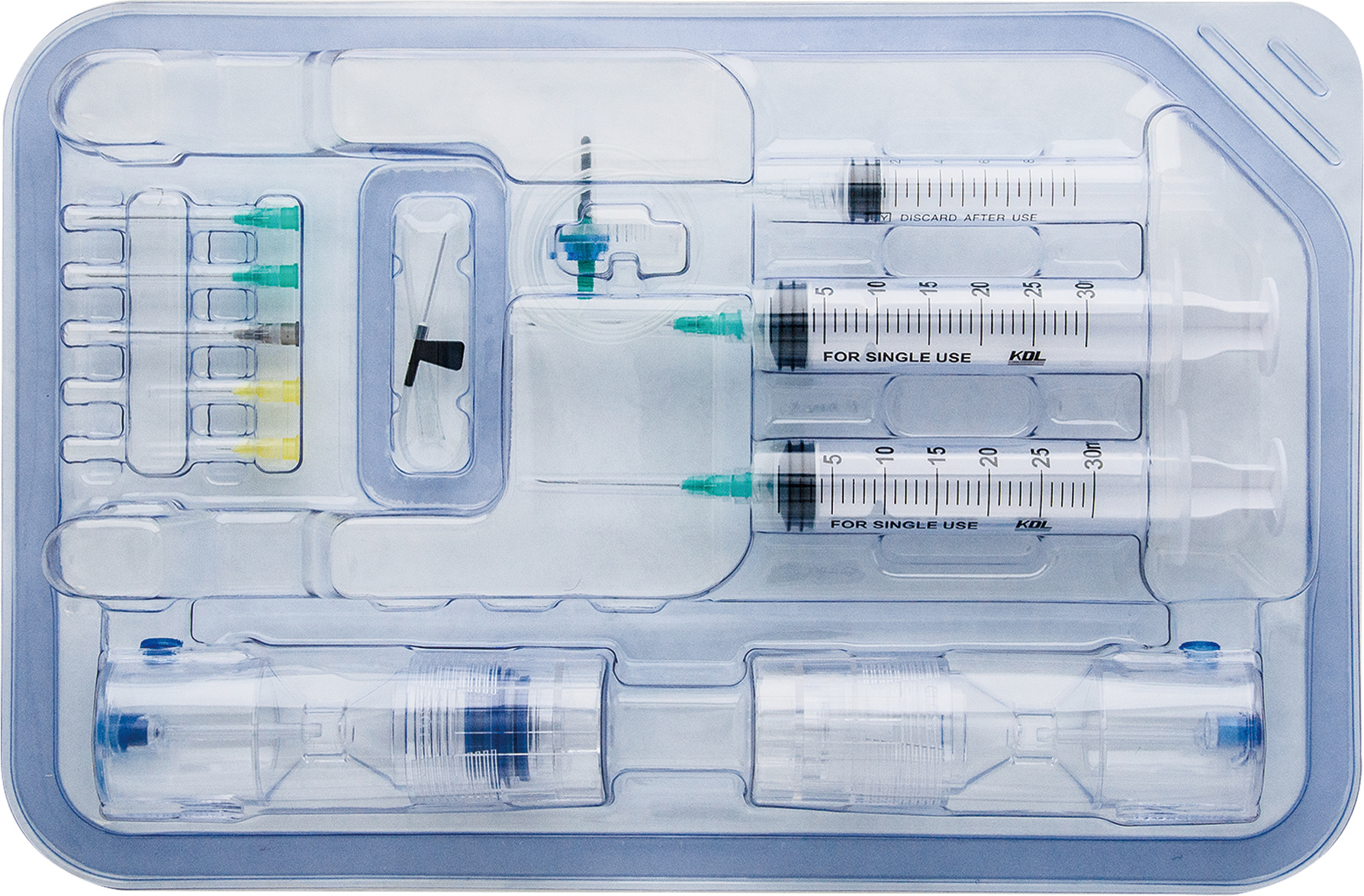
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Preparation Kit
>Fully automatic;
>Platelet concentration is adjustable 2-8 times;
>Safe and reliable;
>Preparation only takes 15 minutes;
>Leukocyte-poor/rich PRP optional;
>Personalized diagnosis and treatment
Application:
Orthopedic(Osteoarthritis; Microfracture surgery; Chronic osteomyelitis)
Rehabilitative Medicine(Meniscal injuries; Rotator cuff injuries; Tennis elbow)
Wound repair(Diabetic foot; Burns; Scalds)
Gynecology(Infertility; Endometrial repair; Improvement of ovarian function)
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery(Anti-aging; Pigmentation; Alopecia areata)
Others(Surgical incisions; Tooth extractions; Dry eye syndrome)
Next article
Related News
PRP Technology – Repair and Anti-Aging
2025-10-14
Clinical Application of PRP in Dermatology
2025-10-10
