
News
Refractory Wounds: Seeing Hope
01 Apr,2025
Refractory wounds refer to the wounds that still cannot be completely repaired in terms of structure and function within the expected time after standardized and systematic treatment. They are usually caused by various factors such as diabetes, infection, pressure injury, etc., and are relatively difficult to treat. The factors that lead to the persistent non-healing of wounds include malnutrition, insufficient tissue perfusion, ischemia-reperfusion, bacterial load and infection, the retention of foreign bodies and necrotic tissues, wound fluid and matrix metalloproteinases, diabetes, cellular senescence, inverted epithelial growth, etc.
With the continuous development of medical technology, new treatment methods and concepts keep emerging, providing more possibilities for the treatment of refractory wounds. Among them, growth factor treatment has received much attention, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment is one of the advanced therapies. Simply put, the PRP technology is to activate the mysterious power hidden in the blood to cure diseases. Platelet-rich plasma treatment (PRP gel) is a jelly-like substance made by extracting platelet-rich bioactive factors from one's own blood and mixing them with activators such as thrombin. This gel has a complete three-dimensional structure and an excellent histocompatible fibrin scaffold, creating a stable environment for tissue repair, so it has been widely used in the field of wound repair.
The main principles of PRP treatment for refractory wounds are as follows:
Promote blood coagulation and hemostasis
PRP contains a high concentration of platelets. When applied to the wound, the platelets will aggregate into clumps locally at the wound site, playing a role in hemostasis and laying the foundation for subsequent repair.
Release growth factors to promote tissue repair
Once the platelets in PRP are activated, various growth factors will be released. These growth factors can induce cell division, differentiation and proliferation, accelerate the natural healing of tissues, promote the proliferation of fibroblasts, enabling them to synthesize more collagen, and accelerate the repair of wounds. They can also stimulate the formation of new blood vessels, improve the blood circulation of the wound, provide nutrients and oxygen for the repair process, which is conducive to tissue regeneration. At the same time, they can promote the proliferation and migration of epithelial cells on the wound, accelerate the epithelialization process, and reduce the risk of infection.
Inhibit the inflammatory response
PRP contains chemokines and active proteins, which can regulate the inflammatory response. When the inflammation is severe, PRP can inhibit excessive inflammation, reduce tissue damage, and create a stable microenvironment for repair.
Enhance local anti-infection ability
A small number of white blood cells in PRP regulate through cytokines and biological proteins to chemotax, aggregate and activate immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils. These cells can phagocytose pathogenic microorganisms, exert an immune response, assist in removing pathogens and necrotic tissues, enhance the local anti-infection ability, and accelerate tissue regeneration and repair.
Provide a repair scaffold and promote wound closure
PRP contains a large amount of fibrin. Fibrin provides a scaffold for repair cells, which is conducive to the attachment, migration and proliferation of cells, and promotes tissue reconstruction. At the same time, fibrin can also contract the wound, promote early closure, and reduce the opportunities for exudation and infection.
Reduce the degree of apoptosis
During wound repair, if the repair cells, inflammatory cells, and extracellular matrix are severely damaged, it will lead to a decline in the function of fibroblasts and an increase in apoptosis, making the wound difficult to heal. Studies have shown that PRP can accelerate cell metabolism, reduce the apoptosis rate, stimulate immature cells to synthesize collagen fibers, and promote the regeneration and repair of damaged tissues.
Platelet-rich plasma treatment (PRP gel) has many advantages. It has obvious therapeutic effects and is safe. It contains many growth factors, hormones, nutrients, protein stabilizers, and other important bioactive compounds, and can be used for cell and tissue regeneration. Its preparation is simple, it causes less trauma to patients, and has a low cost, which can reduce medical expenses. With the continuous development of science and technology, the research on PRP therapy has been continuously deepened and gradually moved towards clinical application. It is expected to become one of the routine clinical treatment methods and bring good news to many patients.
Currently, there is a wide variety of consumables on the market. Shuangwei Biotechnology, having been deeply engaged in the field of blood safety for nearly 30 years, is a leading player in the field of blood transfusion technology in China. It has accumulated rich experience in blood safety management. In order to meet the clinical needs, it has nurtured and incubated a brand-new Class III medical device product, the "Disposable Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation Kit", which obtained a new certificate in September last year.
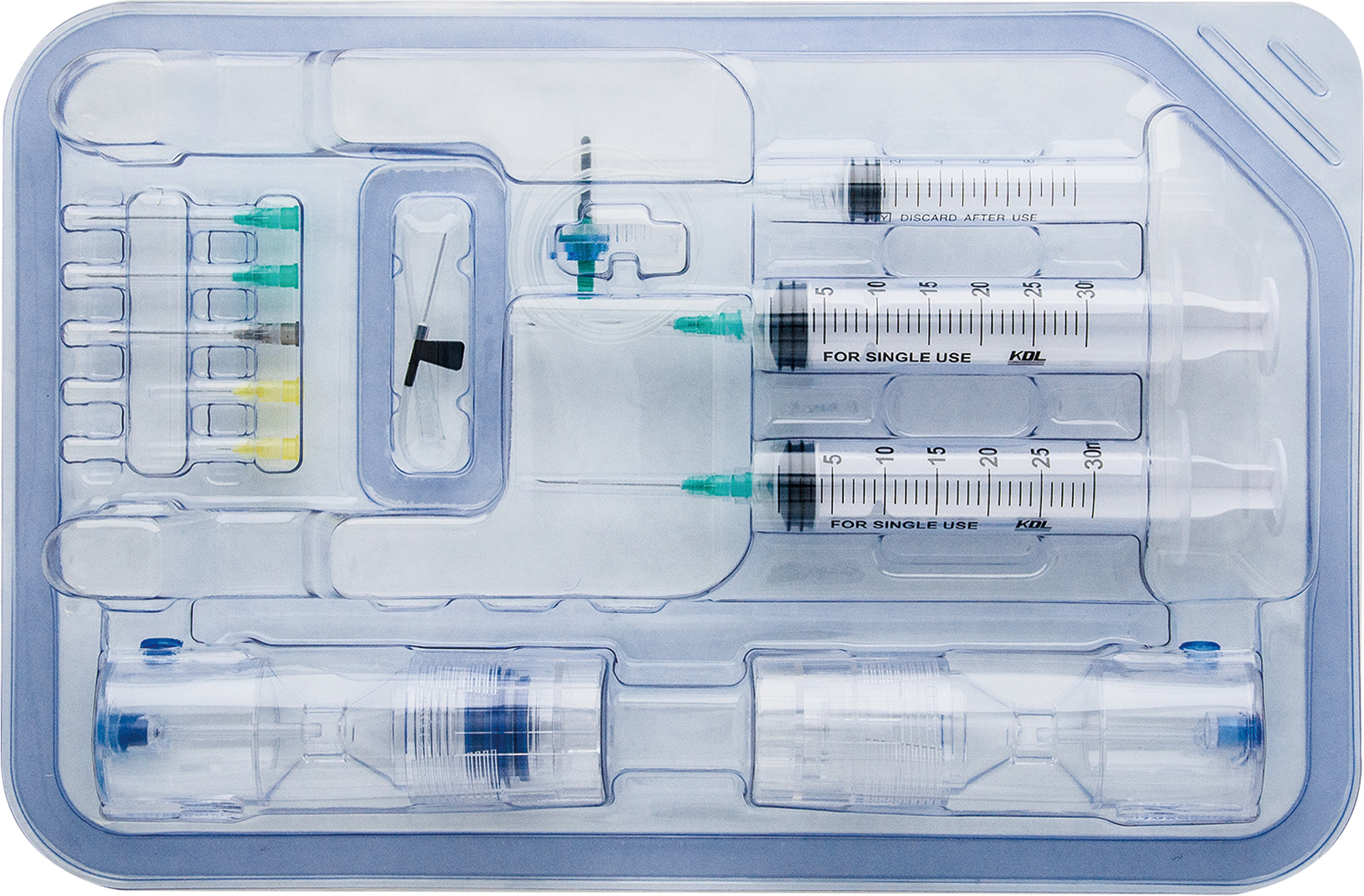
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Preparation Kit
>Fully automatic;
>Platelet concentration is adjustable 2-8 times;
>Safe and reliable;
>Preparation only takes 15 minutes;
>Leukocyte-poor/rich PRP optional;
>Personalized diagnosis and treatment
Application:
Orthopedic(Osteoarthritis; Microfracture surgery; Chronic osteomyelitis)
Rehabilitative Medicine(Meniscal injuries; Rotator cuff injuries; Tennis elbow)
Wound repair(Diabetic foot; Burns; Scalds)
Gynecology(Infertility; Endometrial repair; Improvement of ovarian function)
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery(Anti-aging; Pigmentation; Alopecia areata)
Others(Surgical incisions; Tooth extractions; Dry eye syndrome)
Previous article
Related News

